ECG Quiz 12
ECG Quiz 12
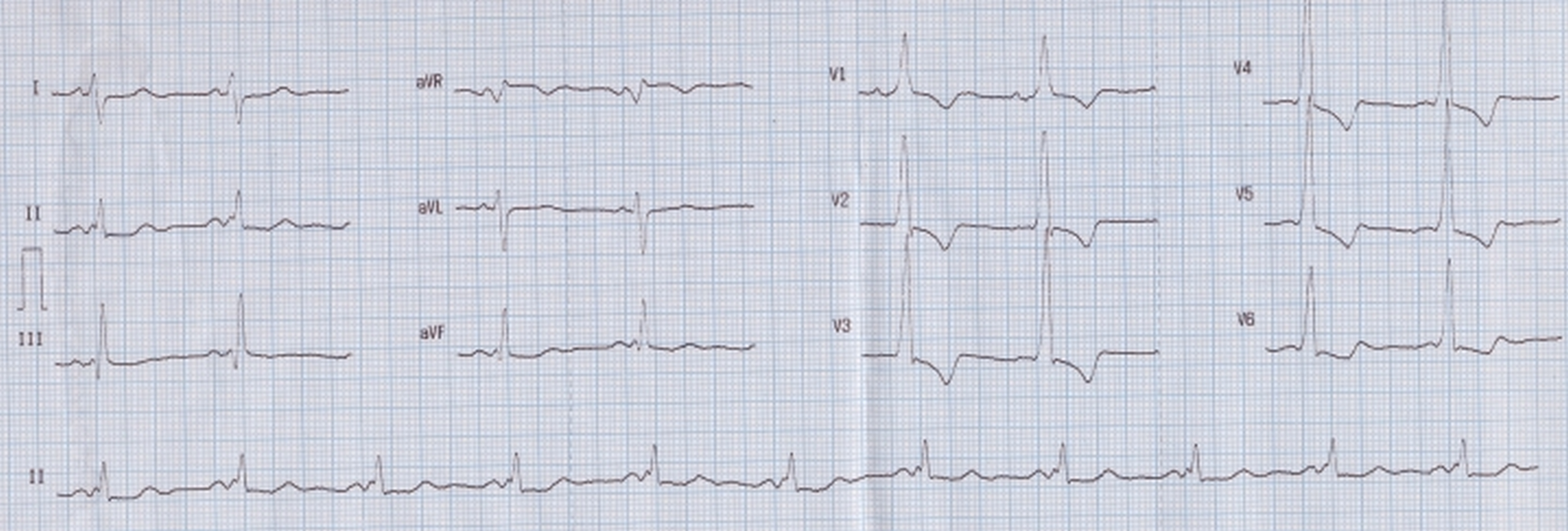
Wolff – Parkinson – White (WPW) syndrome is characterised by a short PR and delta wave with a propensity for arrhythmias. Delta wave is the pre-excitation wave which manifests as a slurred initial portion of the QRS. Since the depolarisation is abnormal, repolarization sequence is altered. Secondary ST – T changes are usual in WPW syndrome. Hence a treadmill test has limited value in checking for inducible ischemia in those with WPW syndrome. The polarity of the delta wave in various leads and the axis helps locating the accessory pathway responsible for the pattern. Paraseptal and free wall pathways have different ECG manifestations. There are various algorithms available for localising the pathway prior to radiofrequency catheter ablation. Risk stratification is needed in asymptomatic WPW syndrome before considering invasive investigations which may include and electrophysiological study. Persons with WPW syndrome are prone for atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia and occasionally atrial fibrillation with a fast ventricular rate. WPW syndrome with atrial fibrillation may lead on to ventricular fibrillation if the ventricle is not able to follow the fast rate. This is more likely to occur if the refractory period of the accessory pathway is low.
Type A wpw