EP tracing in sinus rhythm for AVNRT ablation
EP tracing in sinus rhythm for AVNRT ablation
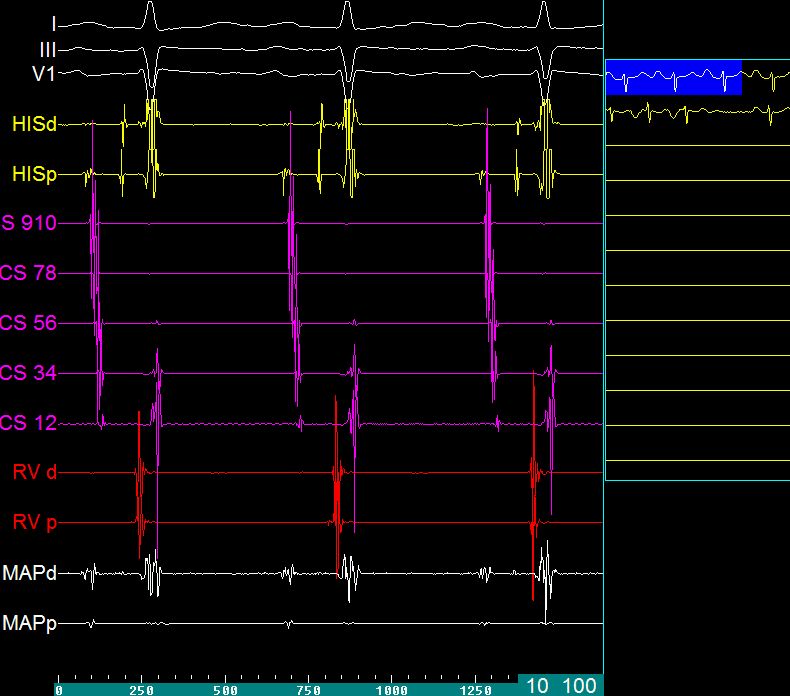
EP tracing in sinus rhythm while planning radiofrequency catheter ablation for AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) in sinus rhythm. Upper three tracing are surface electrocardiograms – leads I, II and V1 (white). Next two tracing are from the His bundle catheter – His distal and proximal. The large broad deflections in this tracing is the V (ventricular electrogram) while the triphasic signal prior to it is the His potential (H). The deflection before that is the atrial electrogram (A). Five pairs of electrodes in coronary sinus are numbered from distal to proximal so that CS 9 – 10 is the proximal pair and CS 1 – 2 is the distal pair, with the other pairs in between. All the tracings from the coronary sinus electrodes are in violet colour. The earliest atrial activity is in the surface lead V1. The atrial activity in the His electrode comes after that, followed by the proximal coronary sinus electrodes. Distal coronary sinus electrodes pick up the atrial activity later, reflecting later activation of the left atrium. The distal coronary sinus electrodes also show the ventricular activity, which is more delayed than the ventricular activity picked by the right ventricular electrodes (RVd: distal; RVp: proximal). The mapping electrode (ablation catheter) picks up atrial and ventricular activities and a tiny His potential. The distal mapping electrode (MAPd) picks up a fractionated atrial electrogram, a tiny His potential and a relatively smaller ventricular electrogram. This type of electrogram is obtained while mapping the potential site for slow pathway ablation, which is between the His bundle catheter and the coronary sinus catheter, in the posterior approach for AVNRT ablation.