PFO Detection by Saline Contrast Echocardiography
PFO detection by saline contrast echocardiography
Patent foramen ovale can cause paradoxical embolism and stroke. Hence in every case of stroke, it is necessary to look for a PFO. PFO typically shunts right to left at the end of a Valsalva maneuver.
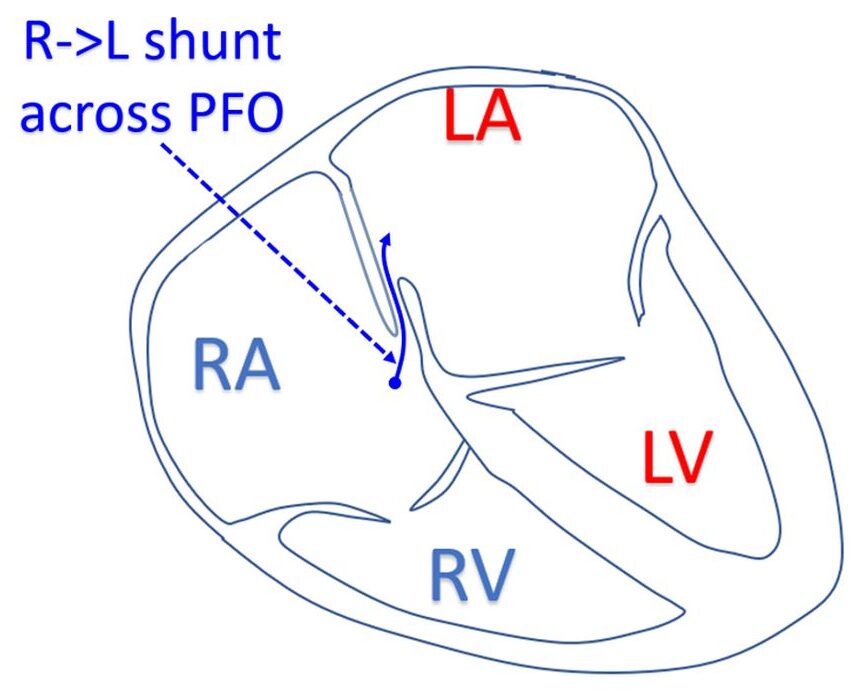
- Hence injection of an agitated saline bolus at the end of a Valsalva maneuver and detection of the microbubbles in the left atrium within three cardiac cycles from the right atrial appearance would suggest presence of a PFO. This is called the “3 beat rule” to discriminate patent foramen ovale mediated right-to-left shunt from intrapulmonary right to left shunt using saline contrast transthoracic echocardiography [1].
- Delayed appearance would indicate a pulmonary arteriovenous fistula.
- Sometimes injection from the lower limb is needed to detect a PFO because of the preferential streaming of the inferior vena caval blood towards the PFO as in fetal life.
- This is more likely if there is an associated Eustachian valve.
- Transesophageal echocardiography may be able to detect PFO better than transthoracic echocardiography.
Reference
- Brett E Fenster, Douglas Curran-Everett, Andrew M Freeman, Howard D Weinberger, J Kern Buckner, John D Carroll. Saline Contrast Echocardiography for the Detection of Patent Foramen Ovale in Hypoxia: A Validation Study Using Intracardiac Echocardiography. Echocardiography. 2014 Apr;31(4):420-7.
