Pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary circulation
Main pulmonary artery (MPA) originates from the right ventricle and its branches take blood to both lungs for oxygenation. Main pulmonary artery divides into left (LPA) and right pulmonary arteries (RPA), which in turn divide into segmental and subsegmental branches. Respiratory gas exchange takes place at the level of the pulmonary capillaries over the alveoli. Oxygenated blood is returned to the pulmonary venous system which drains into the left atrium by four pulmonary veins – right superior, right inferior, left superior and left inferior.
Pulmonary circulation is a low resistance system with pulmonary arterial systolic pressure about one fifth of systemic arterial pressure. Hence right ventricle is a thin walled chamber in the adult, compared to the left ventricle. In fetal circulation, both ventricles are of equal thickness as the pulmonary vascular resistance is high prior to the functioning of the lungs.
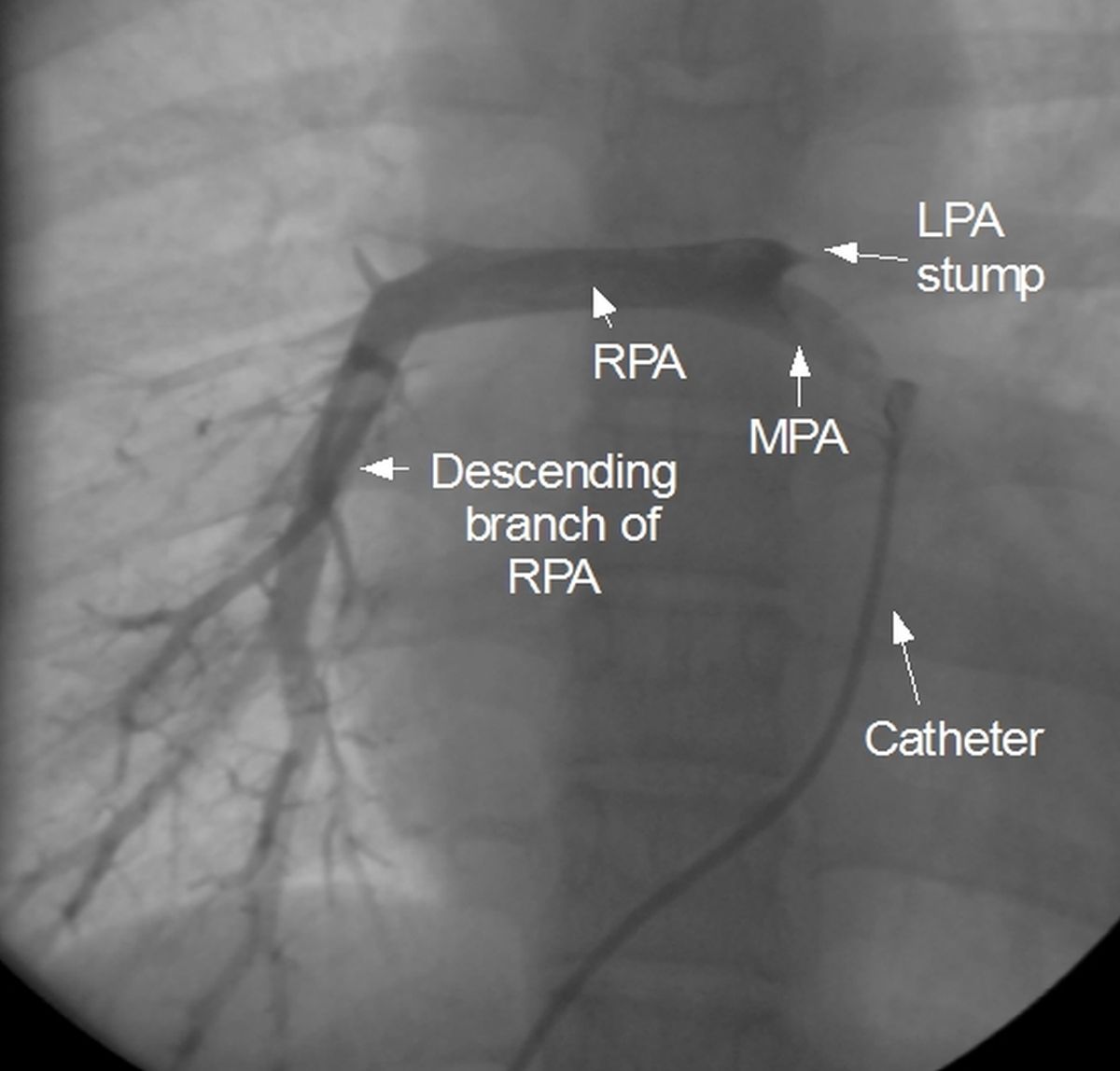 Pulmonary angiogram showing hypoplastic main pulmonary artery and right pulmonary artery. The upper branch of right pulmonary artery is not visible and so is left pulmonary artery. A small stump of left pulmonary artery is visible (see text for abbreviations).
Pulmonary angiogram showing hypoplastic main pulmonary artery and right pulmonary artery. The upper branch of right pulmonary artery is not visible and so is left pulmonary artery. A small stump of left pulmonary artery is visible (see text for abbreviations).