Right atrial overload and right ventricular hypertrophy
Right atrial overload and right ventricular hypertrophy
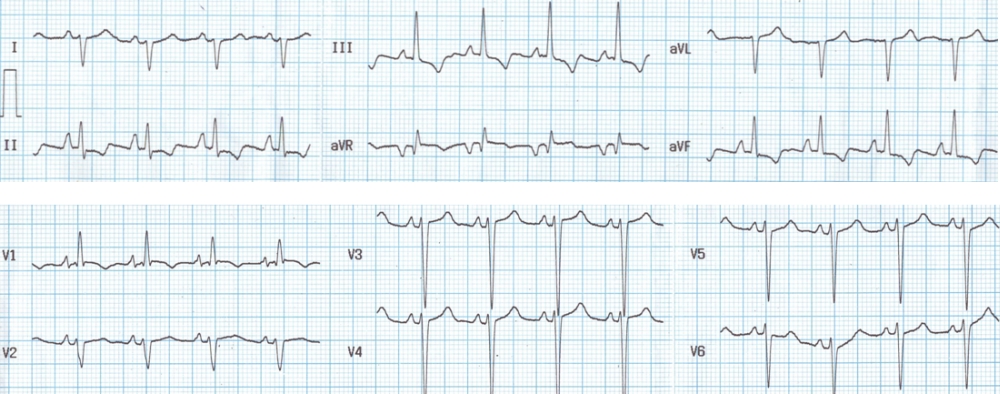
Right atrial overload is manifest as tall sharp P waves in lead II and V1. The cut off values are P wave amplitude more than 0.25 mV in lead II and 0.1 mV in V1. Dominant R waves in V1 and deep S waves in V6 indicate right ventricular hypertrophy. Sokolow-Lyon criteria for RVH mentions that R wave in V1 + S wave in V5/V6 should be 1.1 mV or more. There is also a clockwise rotation in the QRS pattern between V1 to V6. QRS axis is around +120 degrees with aVR biphasic and lead III showing tallest QRS complex. Right axis deviation is also due to right ventricular hypertrophy. T wave inversion in inferior leads and V1 could be due to right ventricular hypertrophy itself.
RVH in this case is type A with dominant R in V1 and deep S in V6. This type is seen in pulmonary stenosis. Type B RVH shows dominant R waves in V1 without deep S in V6. Deep S in V6 without dominant R in V1 seen in chronic obstructive lung disease with cor-pulmonale is called type C RVH. Strictly speaking the types are classified depending upon vector cardiographic features and not based on scalar ECG.

