ROX index
ROX index

ROX index is used to predict the success (and failure) of high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC). ROX index is the ratio of pulse oximetry/fraction of inspired oxygen (FIO2) to respiratory rate. The acronym ROX stands for Respiratory rate and OXygenation.
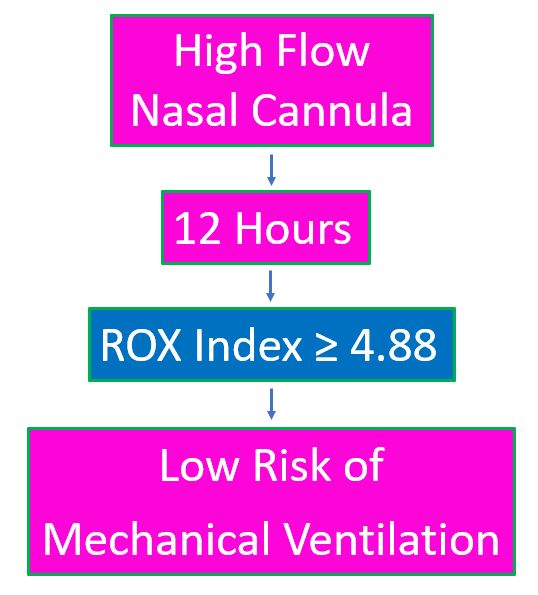
ROX index of 4.88 or more measured after 12 hours of HFNC was associated with a lower risk of mechanical ventilation. This was noted in a study conducted on 157 patients with pneumonia [1]. It was a 4 year observation two center cohort study including patients with severe pneumonia treated with HFNC. 44 patients who needed mechanical ventilation were considered as HFNC failures.
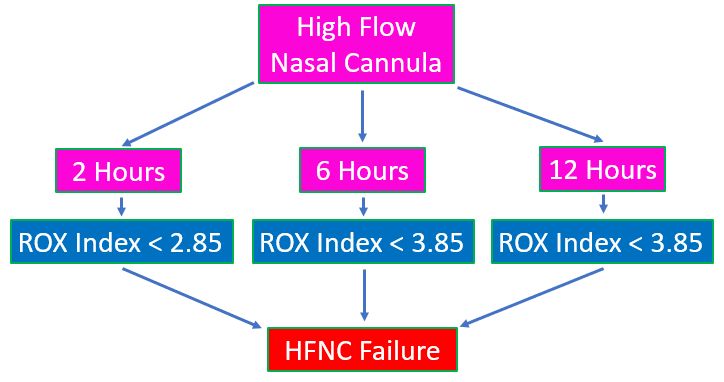
Another study involving 191 patients with pneumonia treated with HFNC showed that prediction accuracy of ROX index increased over time [2]. An index 4.88 or above at two hours had a hazard ratio of 0,434, at 6 hours had hazard ratio of 0,304 and at 12 hours of 0.291. That is a lower risk of intubation while on HFNC. Predictors of HFNC failure were an index less than 2.85 at 2 hours, less than 3.47 at 6 hours and less than 3.85 at 12 hours after initiation of HFNC.
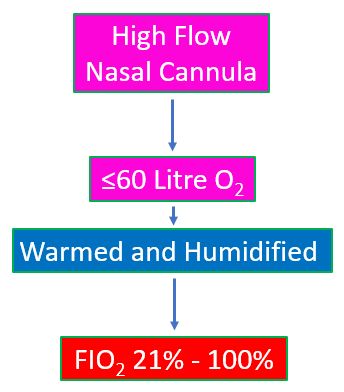
HFNC can delivered up to 60 liters of flow with humidified and warmed oxygen using a special bedside equipment and a large nasal cannula. Fraction of inspired oxygen concentration can be increased up 100% from the 21% available in room air. Due to the large flow, dilution by room air as occurs with conventional nasal oxygen cannula is minimized. This is especially so in patients with respiratory distress who have high minute volumes which tend to dilute oxygen delivered by nasal oxygen by sucking in additional room air.
Reference
- Roca O, Messika J, Caralt B, García-de-Acilu M, Sztrymf B, Ricard JD, Masclans JR. Predicting success of high-flow nasal cannula in pneumonia patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure: The utility of the ROX index. J Crit Care. 2016 Oct;35:200-5.
- Roca O, Caralt B, Messika J, Samper M, Sztrymf B, Hernández G, García-de-Acilu M, Frat JP, Masclans JR, Ricard JD. An Index Combining Respiratory Rate and Oxygenation to Predict Outcome of Nasal High-Flow Therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Jun 1;199(11):1368-1376.