Stenosis of RCA and PDA
Stenosis of RCA and PDA
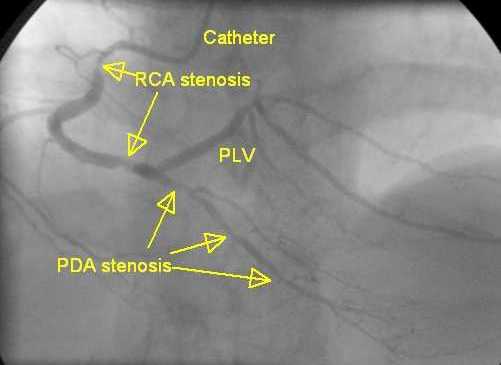
RCA: right coronary artery; PDA: posterior descending coronary artery. PLV: posterior left ventricular branch, also known as PLB.
Right coronary angiogram showing stenosis of RCA and PDA. RCA shows two lesions, one in the proximal region and another distally just before the crux where PDA and PLV branches originate (pre-crux stenosis of RCA). RCA is seen to be a bit tortuous. Difficulty in passing balloons for angioplasty (PTCA balloons) and coronary stents should be anticipated in very tortuous vessels. In such cases the guide catheter tends to back out into the aorta when we try to push the device (balloon or stent) deeper into the vessel. We may need to straighten out the tortuosity using additional stiffer guide wires (buddy wire) or use other techniques like anchor balloon or deep throat the catheter in order to improve guide support during angioplasty / stenting. PDA shows three tandem stenoses from proximal to distal region. PDA appears to be a smaller caliber vessel than PLV. This could also be because the vessel is underfilled due to the tandem stenoses. Very often the vessel size increases remarkably after opening up the lesions by balloon angioplasty / stenting. This is a right dominant system meaning that the right coronary system crosses the crux, the junction of atrioventricular and interventricular grooves posteriorly and supplies the posterolateral region of the left ventricle. It may be noted that even in right dominant systems, the major portion of the left ventricular myocardium is supplied by the branches of the left coronary artery. The term dominance means only an anatomical designation of the artery which crosses the crux to the opposite side.
Right coronary artery supplies the posterior portion of the interventricular septum and gives posterior descending coronary artery in right dominant system [1]. In left dominant system, left circumflex coronary artery supplies this region.
The supply of the posterior interventricular septum is shared by both right coronary artery and left circumflex coronary artery in codominant circulation. About 8% of the population can have left dominance and codominance may be seen in about 7%.
A database of 207 926 percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) for acute coronary syndromes were checked in the CathPCI Registry and reported in 2012 [1]. They noted that left dominance and codominance were associated with modestly increased post PCI in-hospital mortality in patients with acute coronary syndrome.
Reference
- Nisha I Parikh, Emily F Honeycutt, Matthew T Roe, Megan Neely, Eric J Rosenthal, Murray A Mittleman, Joseph P Carrozza Jr, Kalon K L Ho. Left and codominant coronary artery circulations are associated with higher in-hospital mortality among patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention for acute coronary syndromes: report From the National Cardiovascular Database Cath Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (CathPCI) Registry. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012 Nov;5(6):775-82.


