What is the difference between pulsed wave and continuous wave doppler?
What is the difference between pulsed wave and continuous wave doppler?
In pulsed wave Doppler, same piezoelectric crystal is used to transmit and receive the echo from the sample volume. Hence the signals are sent out in pulses and the intervals between the pulses are used to receive the echoes. In continuous wave Doppler, one piezoelectric crystal transmits continuously and another one receives continuously. As the transmission and reception are continuous, it is not possible to find out the depth from which the return signals are received. At the same time continuous wave Doppler can analyze higher velocities while pulsed wave Doppler can analyze only lower velocities.
In case of pulsed Doppler, the maximum velocity which can be analyzed is limited by the Nyquist limit. Nyquist limit is half the pulse repetition frequency. When the velocity of the signal being analyzed, is beyond the Nyquist limit, aliasing occurs so that the exact direction of the signal will be masked.
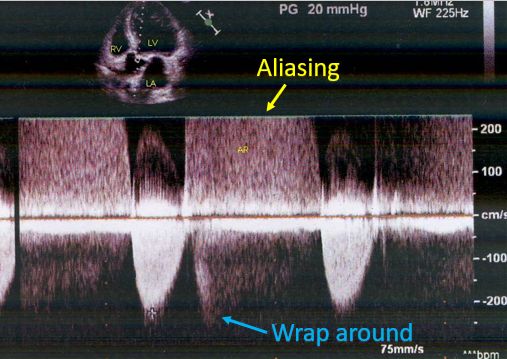
In this image, aortic regurgitation jet is seen as aliased, with part of it above the baseline and part of it below the baseline, which is known as wrap around. In this case, the direction of the jet is towards the transducer and not that of the wrap around, which is seen as away from the transducer. It may be noted that jets towards the transducer are shown above the baseline and those away from the transducer are depicted below the baseline.
Sample volume is the region from which the pulsed Doppler signals are sampled and analyzed. It is shown as a circle along the dotted Doppler line in the image, just beyond the aortic valve. This Doppler tracing is actually from a high pulse repetition Doppler in which multiple sample volumes are analyzed to increase the Nyquist limit. Though high pulse repetition Doppler can analyze higher velocities than simple pulsed Doppler, there is some trade off in the depth perception.
The Doppler line in continuous wave Doppler is usually shown as a continuous line without any sample volume while that in pulsed wave and high pulse repetition Doppler are shown as a dotted lines. Most of the abnormal jets across abnormal valves and those across a ventricular septal defect and patent ductus arteriosus need either continuous wave or high pulse repetition Doppler for analysis due to the high velocity.
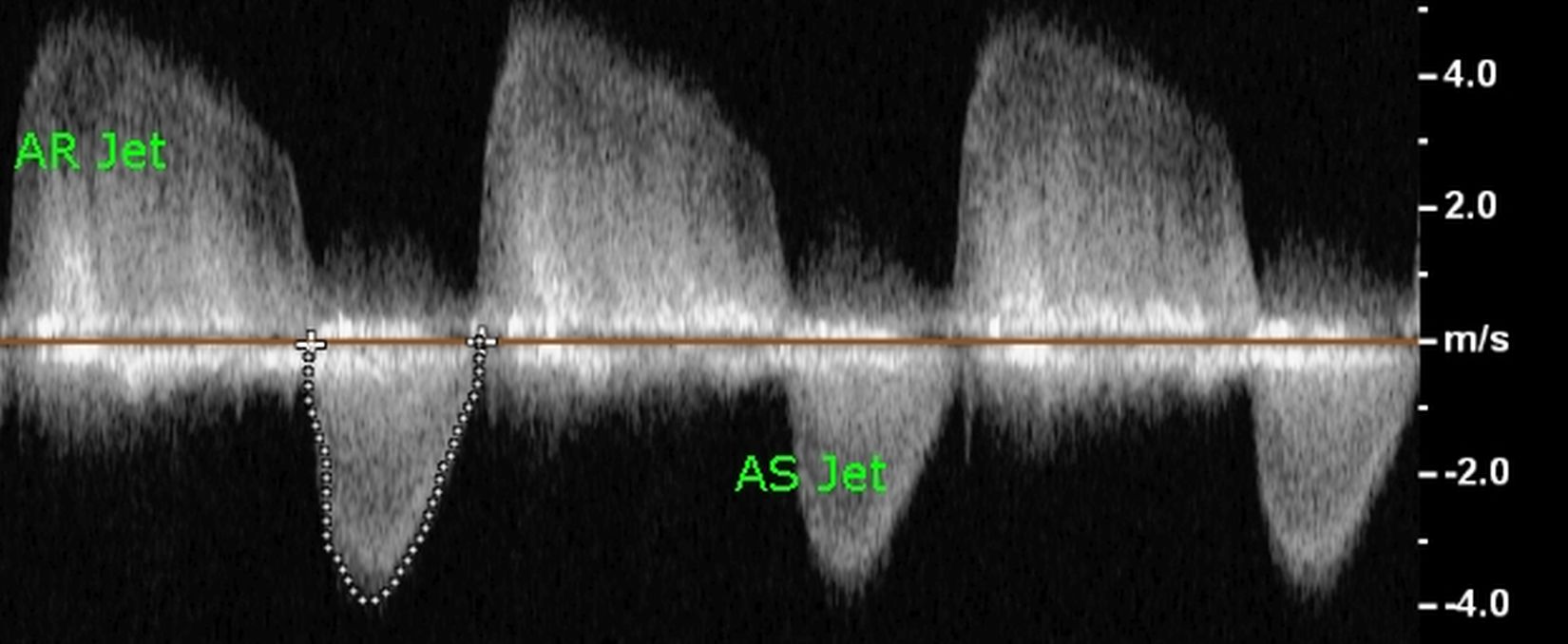
Here is an example of a continuous wave Doppler interrogation of aortic stenosis and regurgitation. Both are high velocity jets and cannot be analysed by pulsed Doppler. Only normal flows across the valves and possibly a low velocity flow across a large atrial septal defect can be measured by pulsed Doppler.

