Arterial tracing in sinus rhythm
Arterial tracing in sinus rhythm
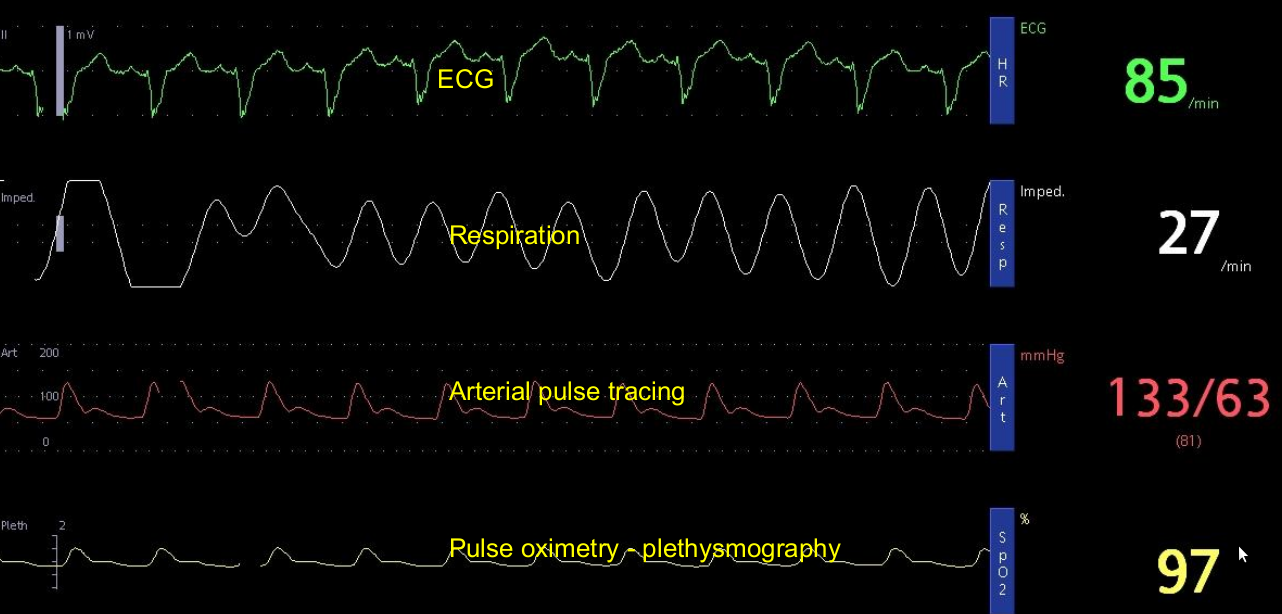
Arterial tracing in sinus rhythm is seen in the third row as a red tracing. The display shows a systolic pressure of 133 mm Hg and diastolic pressure of 63 mm Hg. This type of multiparameter monitoring is now commonplace in any high level intensive care unit. Usually a small arterial cannula is placed in the radial artery and connected to the transducer system kept at the bedside using a fluid filled system. Sometimes when a radial artery is not accessible, femoral or even dorsalis pedis arterial cannula can be used.
ECG tracing shows regular P waves followed by QRS complexes indicating sinus rhythm. The QRS complex is wide, indicating underlying conduction system disease. Heart rate is displayed as 85/minute. The respiratory rate is calculated using dynamic changes in thoracic impedance from the ECG electrodes and is displayed as 27/minute. Impedance is calculated by sending a small current across the chest electrodes. The impedance usually increases with inspiration and decreases with expiration. Pulse oximetry is done using a device kept on a finger in which an infra red light and sensor is used to calculate the dynamic changes in oxygen saturation during each pulse wave. Oxygen saturation is displayed as 97%.

