Atrial Septal Aneurysm
Atrial septal aneurysm
Atrial septal aneurysm is an aneurysmal portion in the region of the fossa ovalis with a diameter of least 1.5 cm and having movement amplitude of at least 1.5 cm or protrusion of at least 1.5 cm (Hanley’s criteria [1]). It is often associated with a patent foramen ovale. It is one of the predisposing factors for paradoxical embolism and stroke. Atrial septal aneurysms can occur in up to 2% of the population.
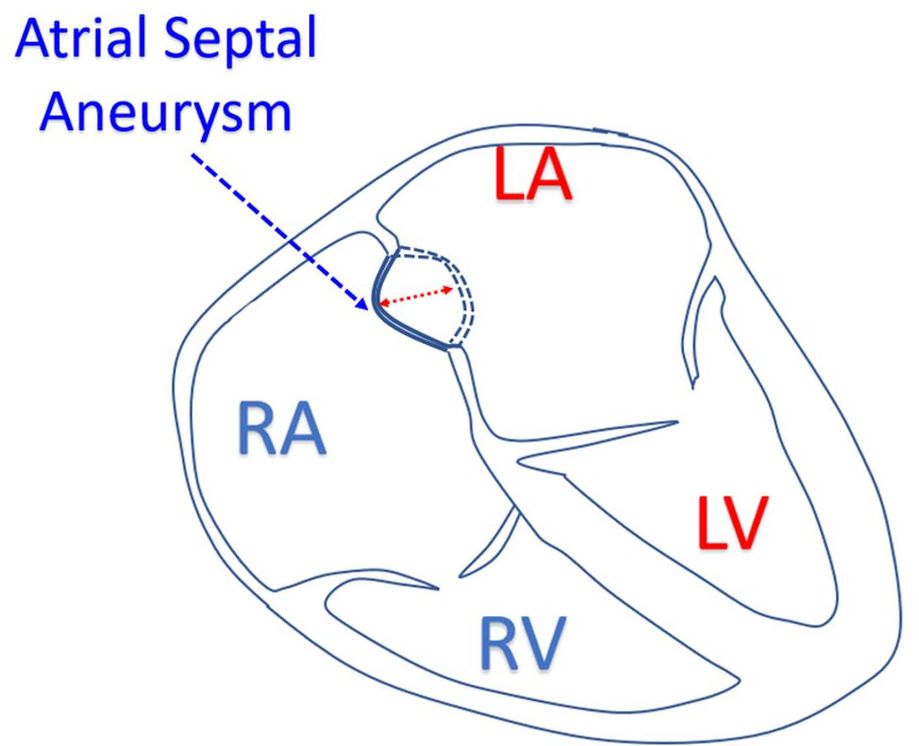
We have to look for atrial septal aneurysm in each case of cryptogenic stroke, preferably by transesophageal echocardiogram. Saline bubble contrast echocardiography should be used to check right to left shunt across a patent foramen ovale [2]. Due to streaming of blood from inferior vena cava, this test may have better outcome if the saline contrast is injected from the lower limb. Atrial septal aneurysm is also visible on transthoracic echocardiography, but visualization of PFO flow details may need transesophageal echocardiography as it has better resolution and echo window.
Razaq et al reported a small IAS aneurysm in a six year old child with left middle cerebral artery stroke [3]. The onset was with vomiting followed by inability to speak and weakness of right side. Computed tomography scan of brain showed ischemic infarct in the left MCA territory. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain confirmed the findings.
Hanley et al have classified atrial septal aneurysms into 3 types: Type 1A, 1B and 2 [1]. Type 1A was fossa ovalis aneurysm with no motion during cardiorespiratory cycle. Type 1B showed rapid phasic oscillation in inspiration, usually confined to the right atrium. Type 2 had markedly redundant fossa ovalis membrane protruding maximally into the left atrium with a total amplitude of phasic excursion more than 1.5 cm.
References
- P C Hanley, A J Tajik, J K Hynes, W D Edwards, G S Reeder, D J Hagler, J B Seward. Diagnosis and Classification of Atrial Septal Aneurysm by Two-Dimensional Echocardiography: Report of 80 Consecutive Cases. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Dec;6(6):1370-82.
- Brett E Fenster, Douglas Curran-Everett, Andrew M Freeman, Howard D Weinberger, J Kern Buckner, John D Carroll. Saline Contrast Echocardiography for the Detection of Patent Foramen Ovale in Hypoxia: A Validation Study Using Intracardiac Echocardiography. Echocardiography. 2014 Apr;31(4):420-7.
- Mohd Razaq, Ravi Kumar Parihar, Ghanshyam Saini. Atrial Septal Aneurysm and Stroke. Ann Pediatr Cardiol. 2012 Jan;5(1):98-9.

