Coronary Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS)
Coronary Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS)
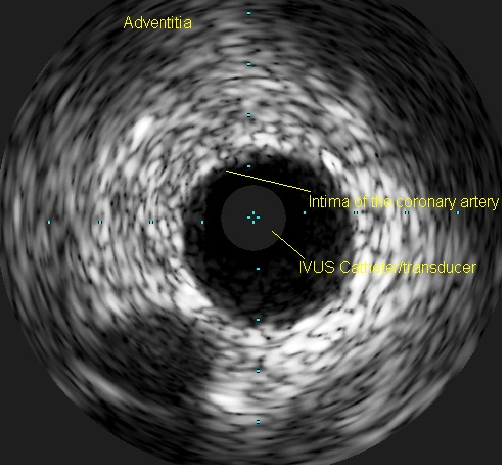
Coronary Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) equipment consists of an IVUS catheter, pullback device and the imaging console. If lesion lengths have to be assessed, motorized pullback is required. For assessing lesion morphology a manual pullback can also be done. While manual pullback allows concentration on specific lesions, it may miss some lesions in between if the pullback is not steady. Catheter has to be disengaged while evaluating coronary ostial lesions.
Heparin and intracoronary nitroglycerine are given before the guide wire is inserted after the coronary cannulation with a guide catheter. The IVUS catheter is then introduced over the guide wire. Images are continuously recorded by the system for later review and analysis.
IVUS Measurements
Measurements include the measurement of lumen, plaque, calcium, remodeling, stent length and volumetric measurements.
Plaque morphology assessment with IVUS
Plaque morphology can be assessed in terms of its geometry and echogenicity. In the geometry, the size of the plaque, its relationship to luminal stenosis, arterial remodeling and eccentricity can be evaluated. Echogenicity could be regarding echolucent and echodense as well as calcified plaques. Thrombus and intimal hyperplasia can be noted. A vulnerable plaque and a plaque with ulceration or rupture can also be found.
Important applications of IVUS
Assessment of an angiographically indeterminate lesion, especially that of left main coronary artery, is an important reason for an IVUS study. It can also give guidance for stenting in terms of assessment of stent apposition and good expansion. IVUS can also delineate intramural hematoma and dissection.
Artifacts in IVUS
Artifacts are possible in an IVUS study due to guide wire artifacts, ring down artifacts, non-uniform rotational distortion, slow flow, coronary pulsation and motion, catheter obliquity and eccentricity and calcium shadow.
Potential complications of IVUS
Major complications are rare and could include dissection or vessel occlusion. But these major complications occur usually during interventions rather than diagnostic IVUS evaluations. Vasospasms are usually transient and respond to intracoronary nitroglycerine. Transient ischemia may occur while negotiating tight stenosis or small vessels. IVUS should be performed only by operators with significant experience in diagnostic and interventional procedures in the coronaries.

