Ostium primum ASD and clinical findings of ASD
Ostium primum ASD and clinical findings of ASD
Ostium primum ASD
Ostium primum atrial septal defect is part of the AV canal defects. In partial AV canal defect, ostium primum ASD is often associated with cleft anterior mitral leaflet producing mitral regurgitation. Tricuspid regurgitation may also be noted. In complete AV canal defect, there is associated canal VSD or inlet VSD and sometimes a single AV valve.
Ostium primum ASD being part of the endocardial cushion defects, may be associated with Down syndrome. They are more likely to develop pulmonary hypertension and Eisenmenger syndrome earlier. DiGeorge syndrome and Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome are the other conditions which can be associated with ostium primum ASD.
Ostium primum ASD is much rarer than ostium secundum ASD. Spontaneous closure is unlikely in ostium primum atrial septal defects.
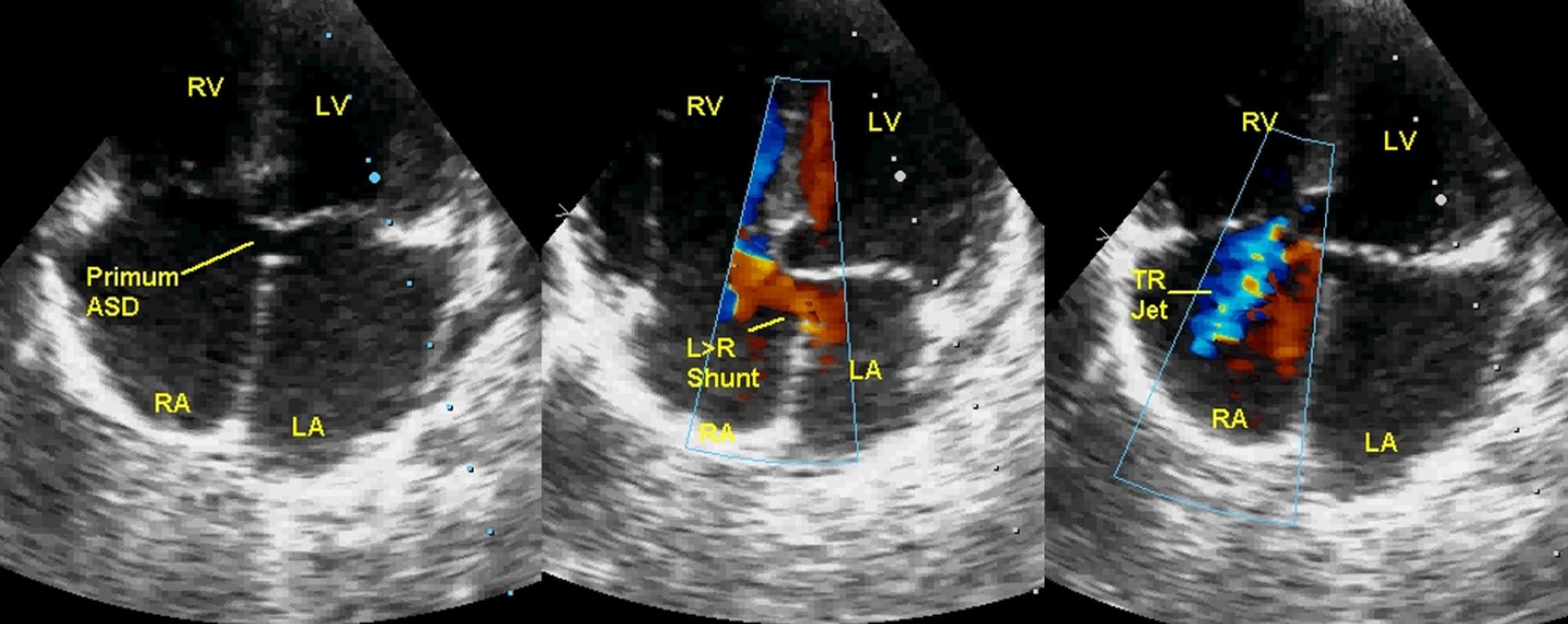
Echocardiogram from the apical four chamber view shows ostium primum ASD seen in the left panel. It may be noted that both AV valves are at the same level (No atrioventricular septum). There is no part of the septum between the ASD and the AV valves, unlike in secundum ASD. Middle panel shows left to right shunt across the ASD (L>R shunt). Right panel shows bluish mosaic tricuspid regurgitation (TR jet). RA: Right atrium, RV: Right ventricle, LA: Left atrium, LV: left ventricle.
Clinical findings in atrial septal defect
Left parasternal pulsations or heave indicate right ventricular enlargement/hypertrophy. Pulsations may also be felt in second left intercostal space due to dilated pulmonary artery. The region may be dull on percussion. Wide fixed split of second heart sound is the auscultatory hallmark of ASD. This is because right ventricular output does not change significantly between inspiration and expiration. In expiration when the right ventricular output is expected to fall, increase in the left to right shunt across the ASD maintains the right ventricular output causing fixity of split. Wide split is because of delayed closure of pulmonary valve due to increased hang out interval in a dilated pulmonary circulation. Pulmonary component of second heart sound (P2) may be loud if there is pulmonary hypertension. Ejection systolic murmur along left sternal border is another finding due to the increased flow across the pulmonary valve. A mid diastolic tricuspid flow murmur may be heard with large shunts, especially in younger individuals. Pansystolic murmur of tricuspid regurgitation is heard with pulmonary hypertension and in AV canal defects. Mitral regurgitation murmur may be associated in AV canal defects with cleft anterior mitral leaflet. Cyanosis can be seen if there is Eisenmenger reaction or sometimes with streaming of inferior vena cava flow by a prominent Eustachian valve into the left atrium across the ASD.