Electrical axis in ECG
Electrical axis in ECG
Electrical axis can be calculated for the P wave, QRS complex, T wave and even the ST segment. But when we mention axis deviation, it is usually the mean electrical axis of the QRS complex. For calculation of mean axis of the QRS complex, the amplitude of the negative waves are subtracted from that of the positive waves while plotting on the graph using lead I as X-axis and aVF as Y-axis. Another method is to check the lead in which transition from positive to negative QRS occurs using the hexaxial reference system. The axis is perpendicular to the lead in which equiphasic complexes are seen.
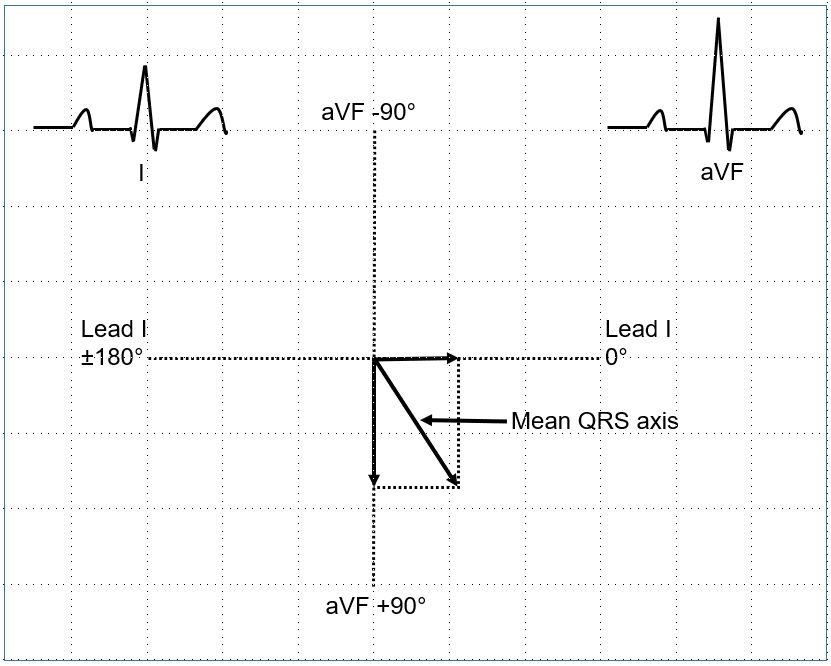
Calculation of axis using lead I and aVF
The axis of lead I is taken as 0° towards the left and ±180° towards the right (negative pole of lead I). The axis of aVF is taken as 90° downwards and -90°in the vertically opposite direction. Mean QRS amplitude of lead I and aVF are plotted along the corresponding axis and the resultant taken as the mean QRS axis.
Calculation of axis using the hexaxial reference system
In the hexaxial reference system, each lead is assigned an axis for its positive pole. The negative pole will be diametrically opposite to it. Mean QRS amplitude in each lead is checked to see if there is a lead in which it is equiphasic. If so, the QRS axis is taken as perpendicular to it. For example, if the equiphasic complexes are found in lead I, QRS axis is 90°. It will be 90° if aVF is positive and -90° if aVF is negative. In this case, aVF will show the longest QRS as the QRS axis is along this lead.
If no lead is seen as equiphasic, leads in between which the QRS transitions from predominantly positive to predominantly negative is checked. Suppose it is between lead II and aVF. Then the transition is at +75°. QRS axis will be -15° if lead I is positive and +165° if lead I is negative.
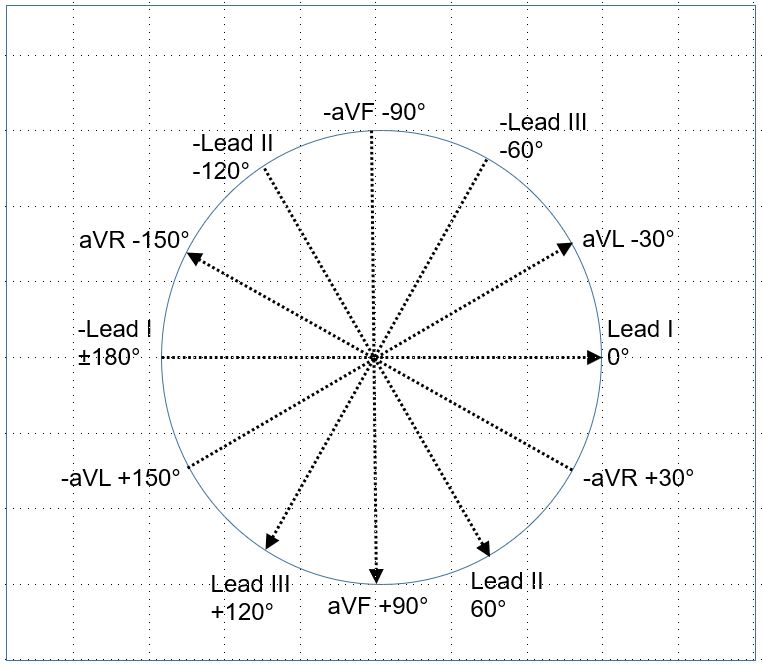
Normal QRS axis is in the right lower quadrant between lead I and aVF. If the axis is in the left upper quadrant between lead I and -aVF, it is taken as left axis deviation. QRS axis up to -30° is taken as minor left axis deviation or leftward axis. QRS axis in the right lower quadrant between aVF and -Lead I is right axis deviation. Axis in the right upper quadrant is indeterminate axis (sometimes called North-West axis). It could occur both in extreme right axis deviation and extreme left axis deviation.
At glance, if both aVF and lead I are positive, the QRS axis is normal. If lead I is negative and aVF is positive, it is right axis deviation. In left axis deviation, lead I is positive and aVF negative. If both lead I and aVF are negative, it is indeterminate or North-West axis.