S1Q3T3 pattern on ECG in pulmonary embolism
S1Q3T3 pattern on ECG in pulmonary embolism
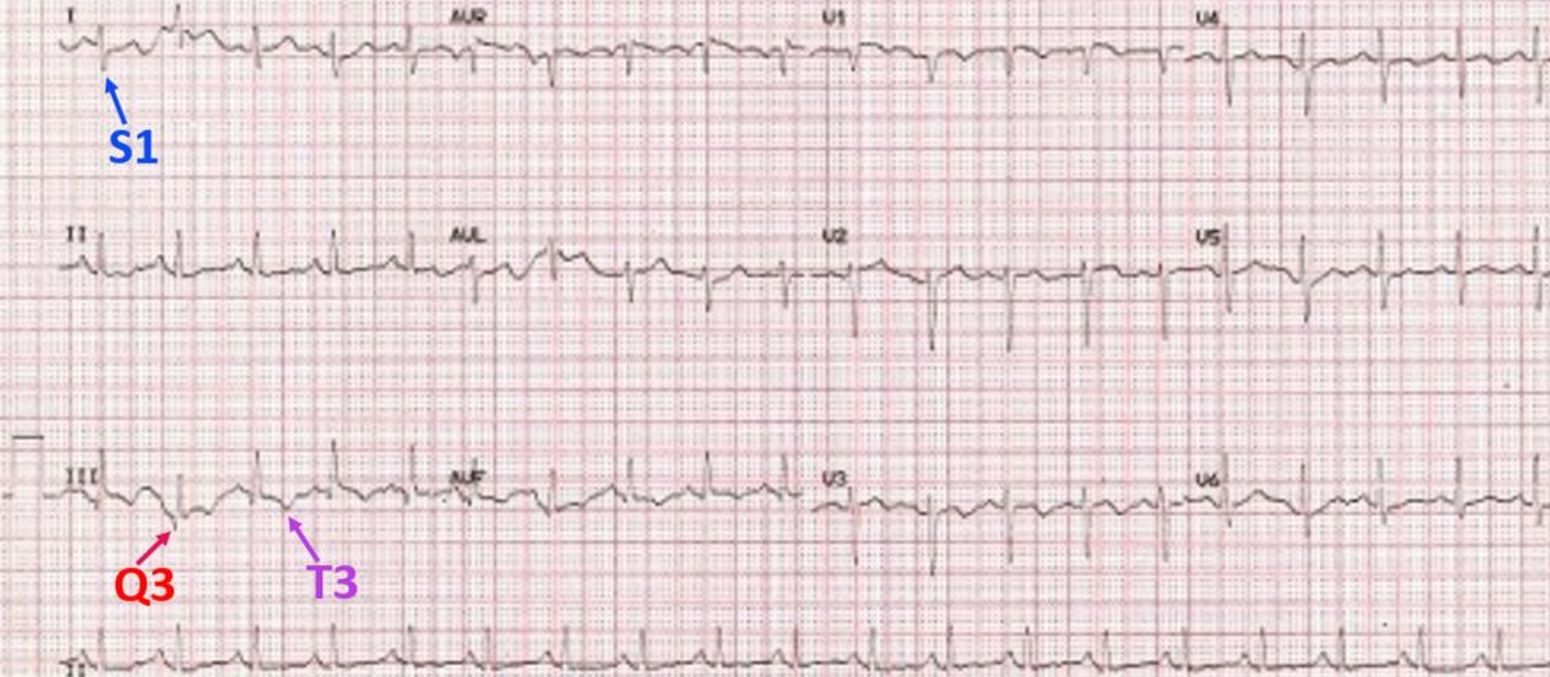 S1Q3T3 pattern in ECG is seen in acute pulmonary embolism [1]. S1Q3T3 pattern means the presence of an S wave in lead I (indicating a rightward shift of QRS axis) with Q wave and T inversion in lead III. S1Q3T3 pattern is the classical ECG pattern of acute pulmonary embolism which is often taught in ECG classes, though it is not the commonest ECG finding in pulmonary embolism. The same pattern can also occur in other cases of acute cor pulmonale.
S1Q3T3 pattern in ECG is seen in acute pulmonary embolism [1]. S1Q3T3 pattern means the presence of an S wave in lead I (indicating a rightward shift of QRS axis) with Q wave and T inversion in lead III. S1Q3T3 pattern is the classical ECG pattern of acute pulmonary embolism which is often taught in ECG classes, though it is not the commonest ECG finding in pulmonary embolism. The same pattern can also occur in other cases of acute cor pulmonale.
The commonest ECG finding in acute pulmonary embolism is sinus tachycardia, which is noted in this ECG as well. T wave inversion in anterior leads is another finding in pulmonary embolism. Incomplete right bundle branch block pattern can also be a manifestation sometimes noted in pulmonary embolism. Both the anterior T wave inversion and incomplete right bundle branch block pattern are indicative of the acute right ventricular overload due to obstruction of pulmonary circulation. ECG changes of acute right ventricular overload resolve rapidly with the resolution of pulmonary embolism by treatment and may return to near normal levels as the pulmonary arterial pressure normalizes.
Similar electrocardiographic findings can also occur rarely in other causes of acute cor pulmonale with right ventricular overload like a major lobar collapse.
Emergency bedside echocardiogram is useful in documenting right ventricular enlargement and increase in right ventricular systolic pressure when ECG shows S1Q3T3 pattern. Right ventricular systolic pressure will be equal to pulmonary artery pressure in the absence of pulmonary stenosis. McConnell sign and 60/60 sign may be present on echocardiography.
Confirmation of pulmonary embolism is by urgent computed tomographic pulmonary angiography. In massive pulmonary embolism, thrombolysis with streptokinase, urokinase, alteplase or tenecteplase, may be considered [2]. Milder cases can be treated with heparin or low molecular weight heparin.
References
- Petruzzelli S, Palla A, Pieraccini F, Donnamaria V, Giuntini C. Routine electrocardiography in screening for pulmonary embolism. Respiration. 1986;50(4):233-43.
- Martin C, Sobolewski K, Bridgeman P, Boutsikaris D. Systemic Thrombolysis for Pulmonary Embolism: A Review. P T. 2016 Dec;41(12):770-775.